For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. Asked Oct 22 2019 in Biology by Shivam01 820k points.
The structure of proteins includes the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary levels.
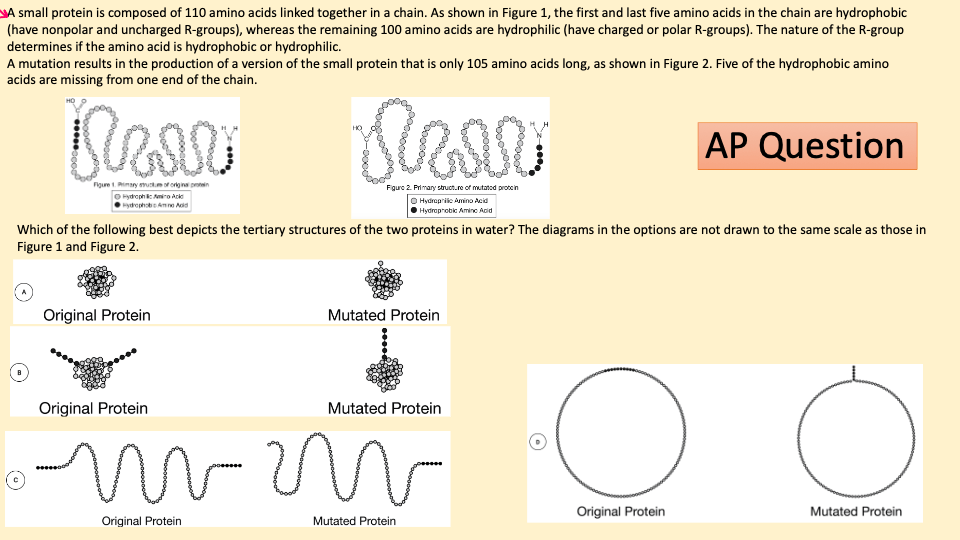
. The forces that stabilize these contacts are. Which of the following best describes tertiary structure. The proteins function in their tertiary structure controlled by temperature pH.
An R-group also called variable group is a side chain that is attached to the α-carbon of the amino acids the building blocks of proteins. The 3-D conformation of a multisubunit protein compose of a number of subunits joined by noncovalent interactions. A interactions between differing subunits of a protein b interactions between α-helixes and β-pleated sheets to form a domain c interactions between amino acids 4 residues away from each other d interactions between single amino acids adjacent to one another.
To some extent the tertiary structure is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure. Bbiology1 415003 which of the following best. After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random.
The tertiary structure of a protein is the set of angles contacts and conformations of all the atoms of a polypeptide chain that give rise to the folding of said polypeptide. It includes alpha helices as a common form. The tertiary structure of the protein is determined by the interactions of the different R-groups with other R-groups and with their environment in the protein Option B.
For instance in globular proteins the polypeptide chains are held together in a definite way forming a compact structure. This is the structure that gives protein the 3-D shape and formation. The polypeptides are the subunits that form the protein molecule.
Click card to see definition. Secondary structure refers to regular recurring arrangements in space of adjacent amino acid residues in a polypeptide chain. The structure formed from interactions between the amino acid side groups is the best statement that describes the tertiary structure of a protein.
BBiology1 415003 Which of the following best describes the tertiary structure of. The secondary structure is a helix or. Hemoglobin is a globular protein composed of a single polypeptide chain that has one O2 binding site.
The tertiary structure consists of eight beta-strands connected by α-helices known as the globin fold B. Which of the following statements describes the tertiary structure of a protein. The polypeptide chain may undergo coiling and folding to produce the tertiary structure.
These structures are stabilised by the several types of bonds namely hydrogen bond ionic bond van der waals interaction covalent bond disulphide bridges and. Local regions of polypeptide chains that have a regular conformation which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The polypeptide chains can be homologous or heterologous.
Protein is one of the four major biomolecules in living systems. The chemical composition of proteins includes amino acids R-groups and a carboxylic acid group. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
The interactions of the different R group with other R groups and with their environment determine the tertiary structure of the protein. The structure formed from interactions between the amino acid side groups. Course Title BIO 183.
It includes beta pleated sheets as a common form. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. Structurally proteins consists of four levels namely.
Tertiary structure of a protein describes A The order of amino acids B Location of. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. Ionic bonds hydrophobic interactions hydrogen bonds disulfide bonds.
Pages 5 Ratings 83 6 5 out of 6 people found this document helpful. What best describes how carbidopa enhances the effect of levodopa. Amino acids linked together in a specific order by peptide bonds.
The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin. Of proteins D The ways of protein folding. The tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional.
The Tertiary Structure of a protein is the arrangement of the secondary structures into this final 3-dimensional shape. Best answer D The ways of protein folding. Which of the following best describes the nature of protein primary structure.
What is the secondary structure of a protein. A The tertiary structure of a protein is the folded structure alpha-helix or beta-sheet formed by additional bonds that are formed in the polypeptide chain. The hydrogen bonds in the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins are directly attacked by.
CIt involves hydrogen bonding between amino acid side- chains. Such inhibitors distort the tertiary protein structure and alter the shape of the active site so the enzyme can no longer bind its substrate so the enzyme cannot catalyze a reaction. Although some non-competitive inhibitors bind reversibly others bind irreversibly and.
It involves hydrogen bonding between the backbone atoms. Tertiary structure is the overall the three-dimension folding driven largely by interactions between R groups. The arrangement is made with the help of chaperones.
The primary structure is a sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds bonded through dehydration synthesis. These secondary structure motifs then fold into an overall arrangement. The linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is.
The sequence of amino acids in a protein the primary structure will determine where alpha helices and beta sheets the secondary structures will occure. The interactions between the side chains in a protein result into its tertiary structure. Quaternary structure of a protein is the way by which two or more polypeptides that make up the protein molecule is arranged.
The polypetides chain that forms a 3-dimensional structure is called as secondary structure. At this level every protein has a specific three-dimensional shape and presents functional groups on its outer surface allowing it to interact with other molecules and giving it its unique function. Several types of side chain interactions stabilize the tertiary structure of proteins including which of the following.
This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins. Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of two different types of globin subunits each of which has an O2 binding site. Specific biological activities such as enzyme activity are associated with the tertiary structure.
Primary secondary tertiary and quartenary. School North Carolina State University. Tap card to see definition.

Solved Which Best Describes Protein Tertiary Structure A The Chegg Com



0 Comments